Teach you how to track geostationary satellites!
chinatopwin
chinatopwin
2017-10-11 10:12:23
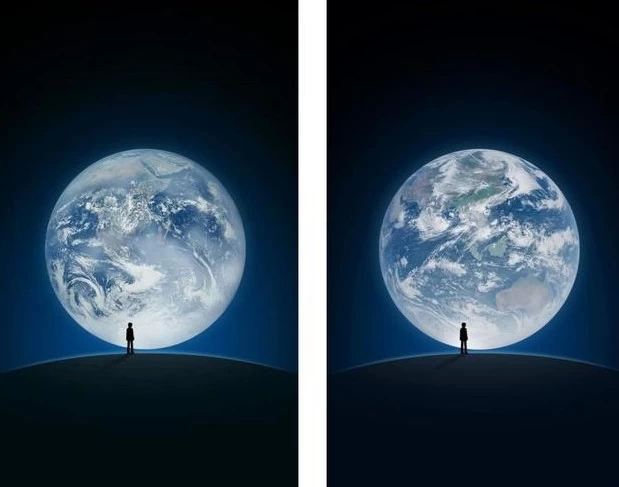
Editor's note: some time ago WeChat login temporarily taken by NASA's famous "Blue Marble"
photos for a new generation meteorological satellite of China and number four star A picture of
the earth, causing the circle of friends to refresh.

As a meteorological satellite, Fengyun four, A, has a orbital altitude of about 35 thousand and
The second week of September, I (Bob King, amateur astronomer and author) a camera
11 geostationary satellites in the picture
On earth, the geostationary satellite (called geostationary satellite) is located in its orbit

Synchronous satellite (here refers to IGSO, which in addition to outside of the geostationary

As a meteorological satellite, Fengyun four, A, has a orbital altitude of about 35 thousand and
800 km. It is actually a geostationary satellite. This paper gives a brief introduction to how to see
the geostationary orbit satellite.
In the sky, there are countless satellites orbiting around the earth day and night. Among them,
In the sky, there are countless satellites orbiting around the earth day and night. Among them,
the geostationary satellite orbiting TV signals is located over the equator and is more than 35
thousand kilometers above the earth. How can we see them?
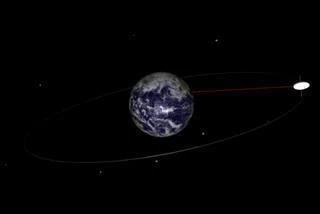
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of geostationary satellite orbit.
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of geostationary satellite orbit.

The second week of September, I (Bob King, amateur astronomer and author) a camera
pointing to the sky just Aquarius (but the sky in a geosynchronous satellite with 2.8), selection
of aperture, ISO400 sensitivity, set the exposure for 3 minutes, then shoot, see if you can take
something interesting some.
Wow... Wow... Wow, look at what I have photographed -- 1 teeth, 2 teeth, 3 teeth. A total of 11
Wow... Wow... Wow, look at what I have photographed -- 1 teeth, 2 teeth, 3 teeth. A total of 11
geostationary satellites point does not move in a row in the picture! After I took a few nights
every night, though the stars are gradually shifting to the west, but they still have the earth
synchronous satellite in the same place. I totally hooked on shooting a geostationary satellite
in this matter.

11 geostationary satellites in the picture
On earth, the geostationary satellite (called geostationary satellite) is located in its orbit
above the equator at a certain point, the period of revolution around the earth and the earth's
rotation cycle exactly the same (is about 24 hours), so (for earth observers) will always point
to a synchronous satellite somewhere above the earth the equator.
Although geostationary satellites do not move from the ground, they actually orbit the earth
Although geostationary satellites do not move from the ground, they actually orbit the earth
at a speed of 11300 kilometers per hour to keep up with the speed of the earth's rotation
As of August 10, 2017, in a geosynchronous satellite with a total of 447 geostationary
As of August 10, 2017, in a geosynchronous satellite with a total of 447 geostationary
satellites in the normal work, but if you count the retired no longer work of satellite
synchronous satellite, the geosynchronous satellite with the distribution of more than 1400.
Each synchronous satellite occupies a narrow strip on the geostationary satellite belt. The
Each synchronous satellite occupies a narrow strip on the geostationary satellite belt. The
length of the narrow strip should be taken into consideration to avoid synchronous
communication interference between satellites and potential collision risks
The geostationary satellite can maintain a position in orbit above the earth's equator always
The geostationary satellite can maintain a position in orbit above the earth's equator always
accurate (the term is maintained by the track), small thrust engine itself from time to time on
the track correction (because the earth's irregular shape lead to changes in the earth's
gravitational field, the magnetic field of the sun and even the moon's gravity factor).

Synchronous satellite (here refers to IGSO, which in addition to outside of the geostationary
satellite synchronous satellite) in the celestial sphere of the analemma slightly than the
equator northerly or southerly point (because its orbit is a very small angle).
Because the geostationary satellite orbit drift will occur because of various factors in the
Because the geostationary satellite orbit drift will occur because of various factors in the
designated position (if not small thrust engine ignition and keep track of the trajectory correction),
so the actual position of the geostationary satellite is often located in a small box.
Using the star simulation software Stellarium to simulate the geostationary satellite belt at 42
degrees north latitude
(the blue line is the celestial equator, the projection of the equator on the celestial sphere; the
(the blue line is the celestial equator, the projection of the equator on the celestial sphere; the
yellow line is the geostationary satellite belt)
Of course, you need to know the local latitude corresponding to the geostationary satellite
Of course, you need to know the local latitude corresponding to the geostationary satellite
band in the sky on the position. For the northern hemisphere stargazers, see the geostationary
satellite in the sky always position in the days of a few degrees south of the equator (see chart),
this is due to the disparity caused.
For example, I (Bob King) location (latitude 47 degrees), synchronous satellite band will appear
For example, I (Bob King) location (latitude 47 degrees), synchronous satellite band will appear
in 7 degrees south of the equator is local, i.e. meridian (in horizontal coordinate system through
the North Pole azimuth circle) 36 degrees high position. The table below it gives a different
latitude in the northern hemisphere, with the correction of geostationary satellite; if you are in
the southern hemisphere, it should be used instead of the correction value.
So when I want to observe the earth synchronous satellite, I will open like Stellarium star
So when I want to observe the earth synchronous satellite, I will open like Stellarium star
simulation software, the first marked a day and then the equator, the equator in the day about 7
degrees on the position of draw a red weft, that is the earth synchronous satellite can see in the
local latitude, find bright stars and easy identification of deep space objects in this latitude line,
position of bright stars or deep space objects in mind.
To go outside to operate a telescope with low magnification field (64 times) (mean field
To go outside to operate a telescope with low magnification field (64 times) (mean field
telescope bigger, have the opportunity to see a synchronous satellite more, the center of the
visual field) to mark the bright star or deep sky objects, and then start shooting, quietly waiting.
Ensure that the telescope on the clock drive or the tracker is closed, it can get better pictures
Ensure that the telescope on the clock drive or the tracker is closed, it can get better pictures
(because the equator closed star tracker, orbit, geostationary satellite orbit is light, no, easy to
identify;If the tracker is not open, the stars orbit, into a spot, and synchronous satellite into
orbit is like a drag, but will darken, is not easy to identify the magnitude of synchronous satellite
in more than 10 -12 between).











